Question 1
A discussion took place on how to improve the management of patients presenting with sepsis. What best describes a care bundle in this scenario
(A) A medical checklist for doctors to ensure that ALL steps are completed in a timely fashion
(B) A group of evidence based processes that are designed to be completed sequentially, and when performed together improves clinical outcomes
(C) A sequence of procedures designed to maximise patient safety
(D) A sequence of procedures designed to optimise allocation of resources
(E) steps in patient management that must be completed sequentially within a defined time period
B: Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain(2012) 12 (4): 199-202.
Question 2
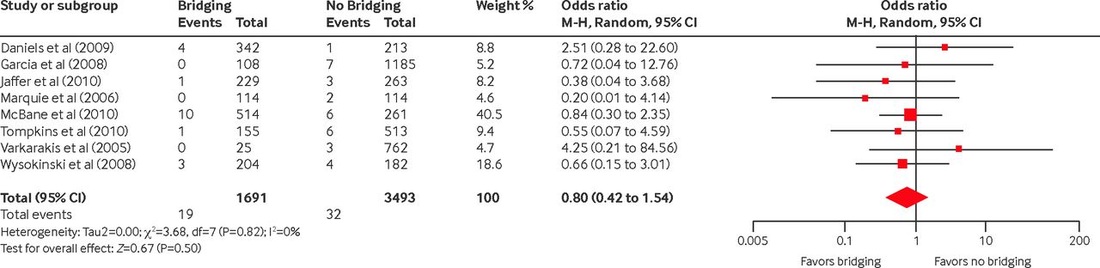
The following table is from Circulation2012;126:1630-9, which depicts a meta-analysis of bridging versus non-bridging strategy for peri-procedural management of warfarin. Bridging therapy is when heparin or clexane is used perioperatively when warfarin is ceased.
A discussion took place on how to improve the management of patients presenting with sepsis. What best describes a care bundle in this scenario
(A) A medical checklist for doctors to ensure that ALL steps are completed in a timely fashion
(B) A group of evidence based processes that are designed to be completed sequentially, and when performed together improves clinical outcomes
(C) A sequence of procedures designed to maximise patient safety
(D) A sequence of procedures designed to optimise allocation of resources
(E) steps in patient management that must be completed sequentially within a defined time period
B: Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain(2012) 12 (4): 199-202.
Question 2
The following table is from Circulation2012;126:1630-9, which depicts a meta-analysis of bridging versus non-bridging strategy for peri-procedural management of warfarin. Bridging therapy is when heparin or clexane is used perioperatively when warfarin is ceased.
Which of the following is an incorrect analysis of this meta-analysis
(A) The heterogeneity of the study is too high to make a decision
(B) The results of the meta-analysis favour bridging therapy
(C) The results of the meta-analysis are inconclusive as to whether one should favour or not favour bridging therapy
(D) The results of the meta analysis shows that bridging therapy is equivalent to non bridging therapy
(E) The results are not valid as odds ratio's were used instead of risk ratio's
D
Question 3
Which of the following is FALSE with regards to survival analysis curves
(A) Hazard ratio's are used in the computation of these curves
(B) Cox-proportional regression analysis are used as a statistical method in the Kaplan-meiyer curves
(C) Time-to-event is a fundamental measure
(D) Survivorship is defined by avoidance of death
(E) Close follow-up of patients is required
D: Survivorship is essentially avoidance of event rather than avoidance of death. PEP 2014
Question 4
In a large randomised control trial of the use of nivolumab in non small cell lung cancer, the methodology reportedly employed a double blinded technique. Which of the following statements is FALSE with regards to this technique in clinical trials
(A) It reduces selection bias
(B) It reduces information bias
(C) It improves internal validity of the study
(D) Both the subject and the investigator are blinded to what the subject receives
(E) Single blinded technique is inferior to a double blinded technique
A: Selection bias is mitigated by entering into strict randomisation of a representative sample. Information bias (or objective bias) occurs when information is collected or analysed in a different matter by the investigator between groups. For example, if investigators are not blinded to an anti-depressant drug, and they are aware of which group is treated, then their interpretation of data may be skewed.
Question 5
The Re-LY trial examined the effects of dabigatran versus warfarin in the prevention of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. An intention to treat analysis was used. What is true with regards to this type of analysis?
(A) It performs analysis on all patients immediately post randomisation who were assigned treatment and control, irrespective of drop out due to side effects and compliance
(B) It avoids introducing bias into the assessment of treatment based on the toxicity of the drug
(C) It reduces information bias
(D) It reduces selection bias
(E) It over-estimates treatment effects
E: Intention to treat analysis is carried on all the patients who were intended to receive the drug, and thus reduces bias (both selection and information). It always under-estimates the effects of treatment and is thought to be a conservative measure.
Question 6
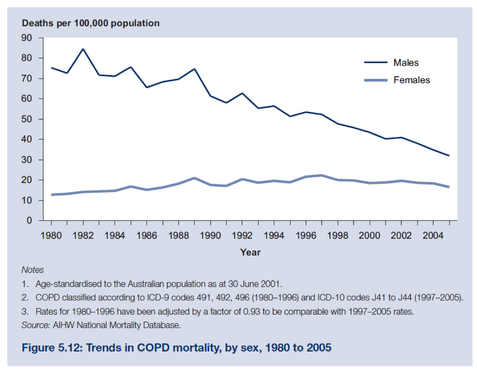
Answer the following question based on the graph presented by AIHW (2008) in relationship to trends associated with COPD in Australia.
(A) The heterogeneity of the study is too high to make a decision
(B) The results of the meta-analysis favour bridging therapy
(C) The results of the meta-analysis are inconclusive as to whether one should favour or not favour bridging therapy
(D) The results of the meta analysis shows that bridging therapy is equivalent to non bridging therapy
(E) The results are not valid as odds ratio's were used instead of risk ratio's
D
Question 3
Which of the following is FALSE with regards to survival analysis curves
(A) Hazard ratio's are used in the computation of these curves
(B) Cox-proportional regression analysis are used as a statistical method in the Kaplan-meiyer curves
(C) Time-to-event is a fundamental measure
(D) Survivorship is defined by avoidance of death
(E) Close follow-up of patients is required
D: Survivorship is essentially avoidance of event rather than avoidance of death. PEP 2014
Question 4
In a large randomised control trial of the use of nivolumab in non small cell lung cancer, the methodology reportedly employed a double blinded technique. Which of the following statements is FALSE with regards to this technique in clinical trials
(A) It reduces selection bias
(B) It reduces information bias
(C) It improves internal validity of the study
(D) Both the subject and the investigator are blinded to what the subject receives
(E) Single blinded technique is inferior to a double blinded technique
A: Selection bias is mitigated by entering into strict randomisation of a representative sample. Information bias (or objective bias) occurs when information is collected or analysed in a different matter by the investigator between groups. For example, if investigators are not blinded to an anti-depressant drug, and they are aware of which group is treated, then their interpretation of data may be skewed.
Question 5
The Re-LY trial examined the effects of dabigatran versus warfarin in the prevention of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. An intention to treat analysis was used. What is true with regards to this type of analysis?
(A) It performs analysis on all patients immediately post randomisation who were assigned treatment and control, irrespective of drop out due to side effects and compliance
(B) It avoids introducing bias into the assessment of treatment based on the toxicity of the drug
(C) It reduces information bias
(D) It reduces selection bias
(E) It over-estimates treatment effects
E: Intention to treat analysis is carried on all the patients who were intended to receive the drug, and thus reduces bias (both selection and information). It always under-estimates the effects of treatment and is thought to be a conservative measure.
Question 6
Answer the following question based on the graph presented by AIHW (2008) in relationship to trends associated with COPD in Australia.
(A) There is a statistically significant decrease in the trend of males dying of COPD related lung disease
(B) There is a statistically significant increase in females dying of COPD related lung disease
(C) The decrease in male death rates is due to decreased smoking uptake
(D) Females have a lower death rate than males at the time of publication (2008)
(E) It is likely that in 2050 females will overtake males in terms of COPD related death rates
D: A and B are incorrect as there is no statistical analysis performed to justify the statement. If there is a regression curve and that regression co-efficient was statistically significant then A or B could be correct. C is making an assumption, although it is likely to be correct. Again E is making an extrapolation too far out.
Question 7
What is Australia's population according to the Australian Bereau of Statistics in June, 2015
(A) 20 000 000
(B) 21 500 000
(C) 23 000 000
(D) 23 700 000
(E) 24 200 000
D: http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/[email protected]/mf/3101.0
(B) There is a statistically significant increase in females dying of COPD related lung disease
(C) The decrease in male death rates is due to decreased smoking uptake
(D) Females have a lower death rate than males at the time of publication (2008)
(E) It is likely that in 2050 females will overtake males in terms of COPD related death rates
D: A and B are incorrect as there is no statistical analysis performed to justify the statement. If there is a regression curve and that regression co-efficient was statistically significant then A or B could be correct. C is making an assumption, although it is likely to be correct. Again E is making an extrapolation too far out.
Question 7
What is Australia's population according to the Australian Bereau of Statistics in June, 2015
(A) 20 000 000
(B) 21 500 000
(C) 23 000 000
(D) 23 700 000
(E) 24 200 000
D: http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/[email protected]/mf/3101.0