Question 1
Which of the following pathophysiological hallmarks differentiate giant cell arteritis from polymyalgia rheumatica?
(A) dendritic cell involvement
(B) Th1/ INF-beta/ IL-12 response
(C) Th17/ IL17/ IL-6 response
(D) Raised ESR
(E) Raised CRP
B: Giant cell arteritis tends to have both Th1 and Th17 type responses, with only the later being steroid sensitive and suppressible. PMR tends to involve Th17 response, being exquisitely steroid sensitive. N Engl J Med 2014; 371:50-57, PEP lectures 2014
Question 2
Which of the following is NOT a pathological abnormality that occurs in giant cell arteritis
(A) involvement of the internal elastic lamina
(B) predominant dendritic cell response
(C) smooth muscle and fibroblast proliferation
(D) granulomatous inflammation
(E) predominant Th2 driven inflammatory response
E: N Engl J Med 2014; 371:50-57
Question 3
Which HLA allele is associated with a poorer visual symptom prognosis in giant cell arteritis?
(A) HLA B5
(B) HLA DR2/ DQ8
(C) HLA DQ1
(D) HLA B57
(E) HLA DRB1*04
E: N Engl J Med 2014; 371:50-57
Question 4
Which of the following antibodies is associated with scleroderma renal crisis?
(A) centromere
(B) scl70
(C) U3-RNP
(D) ANA
(E) RNA-polymerase III
E: Anti-centromere is associated with limited scleroderma, having a better prognosis and less ILD. Anti Scl70 is associated with diffuse scleroderma and ILD. U3-RNP is associated with SLE, mixed connective tissue disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension in an African-American population. RNA-polymerase III is associated with diffuse cutaneous involvement and scleroderma renal crisis. BMJ 2015;351:h5079
Question 5
Which of the following is NOT associated with RNA-polymerase III antibodies?
(A) Diffuse scleroderma
(B) Megaloblastic anaemia
(C) Iron deficiency anaemia
(D) scleroderma renal crisis
(E) gastric astral vascular ectasia
B: RNA polymerase is associated with GAVE, which may predispose to iron deficiency anaemia in patients with scleroderma. J Rheumatol 2014;41:99-105
Question 6
Which of the following antibodies are NOT found in dermatomyositis or polymyositis?
(A) Anti-SRP
(B) Anti-Jo1
(C) Anti-OJ
(D) Anti-CJ
(E) Anti-Mi2
D: Anti-Sdnthetase antibodies are the most common antibodies found and include Anti-Jo1, Anti-PL12, anti-PL7, Anti-OJ and anti-EJ. Anti-Mi2 is related to dermatomyositis and has a good prognosis. The most common anti-synthetase antibody is anti-Jo-1, which targets histidyl-tRNA synthetase. Autoimmun Rev2014;13:883-91
Question 7
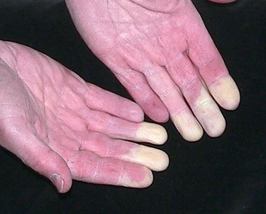
The following is a picture of a patient's hand, courtesy of sticksite.com.
Which of the following pathophysiological hallmarks differentiate giant cell arteritis from polymyalgia rheumatica?
(A) dendritic cell involvement
(B) Th1/ INF-beta/ IL-12 response
(C) Th17/ IL17/ IL-6 response
(D) Raised ESR
(E) Raised CRP
B: Giant cell arteritis tends to have both Th1 and Th17 type responses, with only the later being steroid sensitive and suppressible. PMR tends to involve Th17 response, being exquisitely steroid sensitive. N Engl J Med 2014; 371:50-57, PEP lectures 2014
Question 2
Which of the following is NOT a pathological abnormality that occurs in giant cell arteritis
(A) involvement of the internal elastic lamina
(B) predominant dendritic cell response
(C) smooth muscle and fibroblast proliferation
(D) granulomatous inflammation
(E) predominant Th2 driven inflammatory response
E: N Engl J Med 2014; 371:50-57
Question 3
Which HLA allele is associated with a poorer visual symptom prognosis in giant cell arteritis?
(A) HLA B5
(B) HLA DR2/ DQ8
(C) HLA DQ1
(D) HLA B57
(E) HLA DRB1*04
E: N Engl J Med 2014; 371:50-57
Question 4
Which of the following antibodies is associated with scleroderma renal crisis?
(A) centromere
(B) scl70
(C) U3-RNP
(D) ANA
(E) RNA-polymerase III
E: Anti-centromere is associated with limited scleroderma, having a better prognosis and less ILD. Anti Scl70 is associated with diffuse scleroderma and ILD. U3-RNP is associated with SLE, mixed connective tissue disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension in an African-American population. RNA-polymerase III is associated with diffuse cutaneous involvement and scleroderma renal crisis. BMJ 2015;351:h5079
Question 5
Which of the following is NOT associated with RNA-polymerase III antibodies?
(A) Diffuse scleroderma
(B) Megaloblastic anaemia
(C) Iron deficiency anaemia
(D) scleroderma renal crisis
(E) gastric astral vascular ectasia
B: RNA polymerase is associated with GAVE, which may predispose to iron deficiency anaemia in patients with scleroderma. J Rheumatol 2014;41:99-105
Question 6
Which of the following antibodies are NOT found in dermatomyositis or polymyositis?
(A) Anti-SRP
(B) Anti-Jo1
(C) Anti-OJ
(D) Anti-CJ
(E) Anti-Mi2
D: Anti-Sdnthetase antibodies are the most common antibodies found and include Anti-Jo1, Anti-PL12, anti-PL7, Anti-OJ and anti-EJ. Anti-Mi2 is related to dermatomyositis and has a good prognosis. The most common anti-synthetase antibody is anti-Jo-1, which targets histidyl-tRNA synthetase. Autoimmun Rev2014;13:883-91
Question 7
The following is a picture of a patient's hand, courtesy of sticksite.com.
Which of the following medications does not have evidence to support its use primary for this treatment?
(A) Nitrates
(B) Sildafenil
(C) Amlodipine
(D) Fluoxetine
(E) Hydroxychloroquine
E: Lancet 1995; 345:1378. - evidence for SSRIs
Question 8
Rheumatoid factor is associated with both connective tissue disease and non-connective tissue disease. Which of the following non connective tissue diseases is rheumatoid factor LEAST found in?
(A) Hepatitis B
(B) Hepatitis C
(C) TB
(D) Silicosis
(E) Cryoglobulinaemia
B: Am J Med 1991 91:528
(A) Nitrates
(B) Sildafenil
(C) Amlodipine
(D) Fluoxetine
(E) Hydroxychloroquine
E: Lancet 1995; 345:1378. - evidence for SSRIs
Question 8
Rheumatoid factor is associated with both connective tissue disease and non-connective tissue disease. Which of the following non connective tissue diseases is rheumatoid factor LEAST found in?
(A) Hepatitis B
(B) Hepatitis C
(C) TB
(D) Silicosis
(E) Cryoglobulinaemia
B: Am J Med 1991 91:528