Diagnosis of Asthma
- Wrong Dx is often made - 12% ERJ 2003 Robinson et al
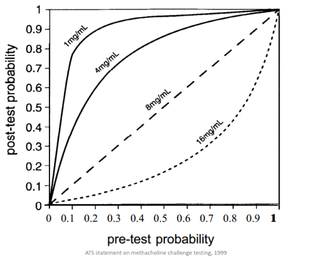
- Need compatible history (intermittent chest tightness, wheeze, dyspnoea, cough, exposure history) to give the right pre-test probability AND either (1) Bronchodilator reversibility (2) Variability or (3) inducibility
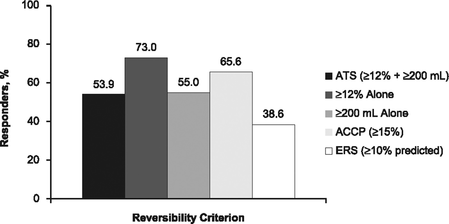
- Bronchodilator reversibility: ATS criterion 12% and 200mL in either of FEV1 or FVC
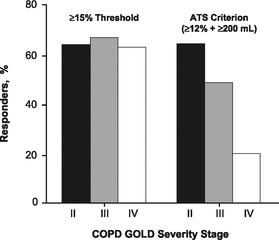
- By itself not sufficient to make a Dx - can be seen in COPD (see TORCH study, where patients can move in and out of BR) - See figure below. Incidence of reversibility inversely proportional to COPD severity.
- Up to 42% of patients with COPD can demonstrate BR http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.10-2974
- Reversibility status changes in up to 50% of patients with COPD between clinic visit
- Bronchodilator reversibility: ATS criterion 12% and 200mL in either of FEV1 or FVC
- Inducibility
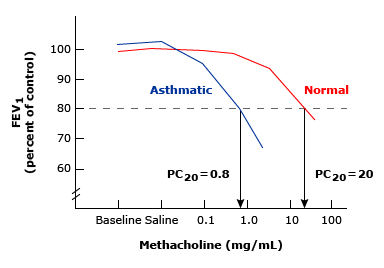
- This is performed through tests to assess for airway hyper-responsiveness - concept that asthmatics have a more highly responsive airway
- Direct challenge test: histamine or methacholine challenge
- Indirect challenge test: mannitol
|
- Variability using peak flow tools
- Very effort dependent, cannot check how good the blow is as you can with spirometry (flow vs time curve)
- Spiro can be grossly abnormal whilst peak flows still within normal range, therefore can cause under-estimation of severity
- Use of exhaled nitric oxide
- Not well validated for the diagnosis of asthma - some role in predicting eosinophilic inflammation
- NO has many functions, including vasodilating, bronchodilating, neurotransmission and co-ordination of cilia beat frequency
- NO is produced through Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) of which there are three isoforms - neuronal NOS, inducible NOS and endothelial NOS.
- nNOS and eNOS are constitutively active, whilst iNOS is induced on endothelial surface by inflammatory cytokines [IL-1, IL4, IL13], reduced by glucocorticoids, bacteria, tobacco smoke
- Ongoing research as to its utility in management
- Have used FeNO based Rx for severe asthma in pregnancy – fewer exac (NNt = 6), improved qol, better neonatal outcomes
- Have used FeNO based Rx for severe asthma in pregnancy – fewer exac (NNt = 6), improved qol, better neonatal outcomes
Airway hyper-responsiveness
- Anne woolcock was one of the first people to measure airway hyper-responsiveness. In her initial experiments, she found that the response to histamine in asthmatic airways was more sensitive and did not have a plateau.
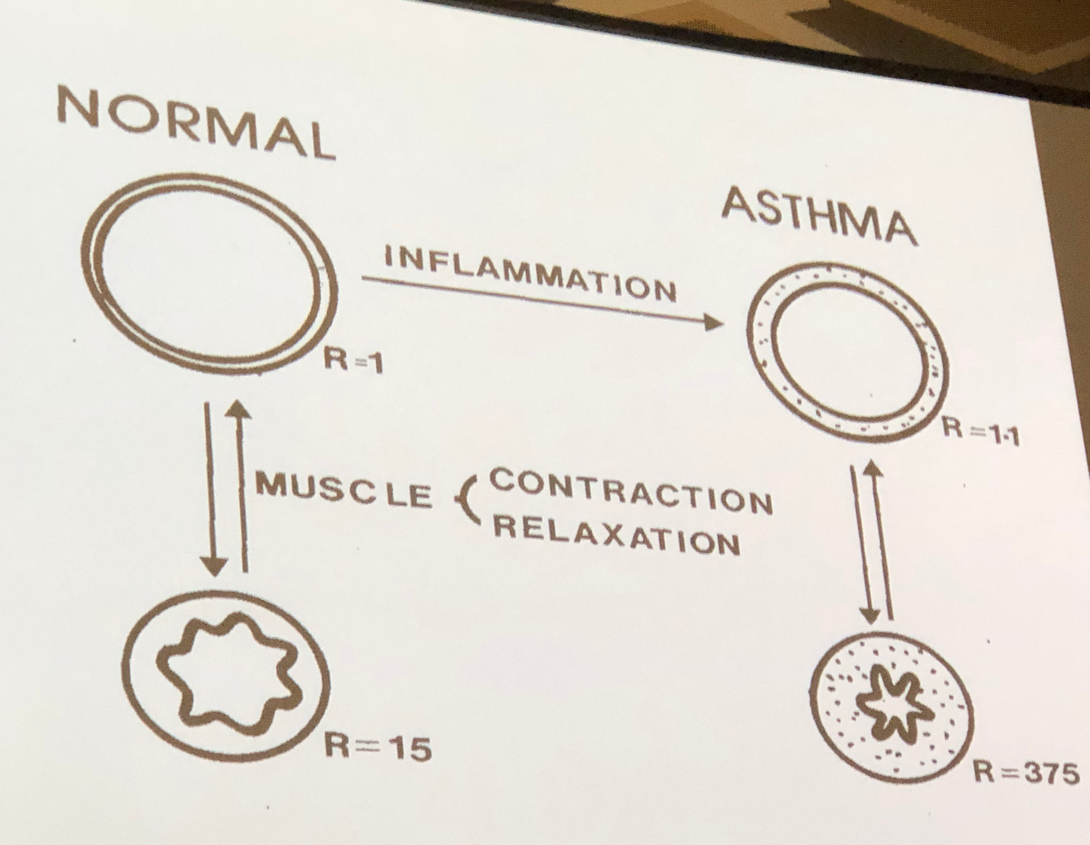
- Asthmatic airways are not just hyper-responsive, but they have evidence of remodelling both in large and small airways.
|
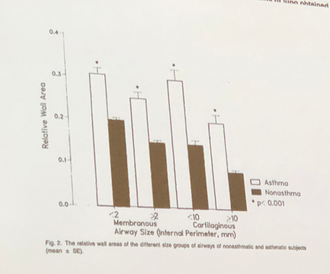
Changes in wall thickness represent changes not just in airway smooth muscle but also extracellular matrix.
|
|
Inhaler Science in relation to asthma
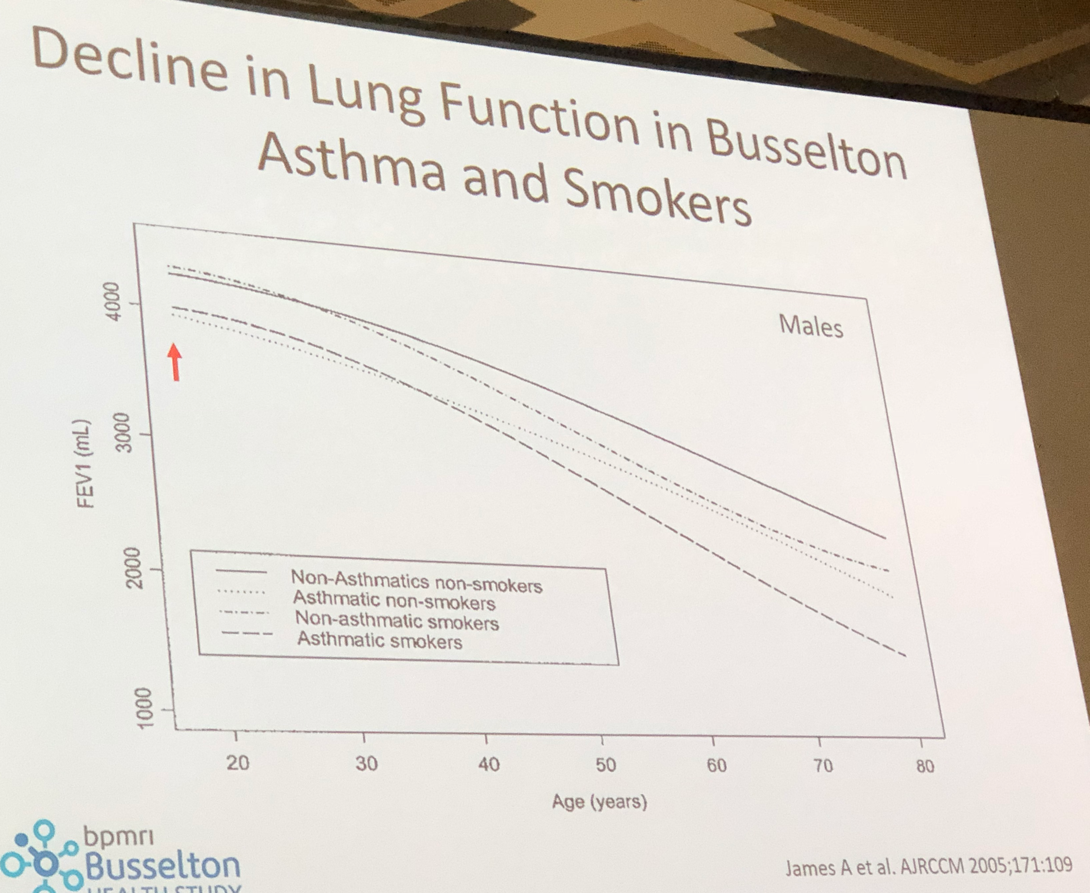
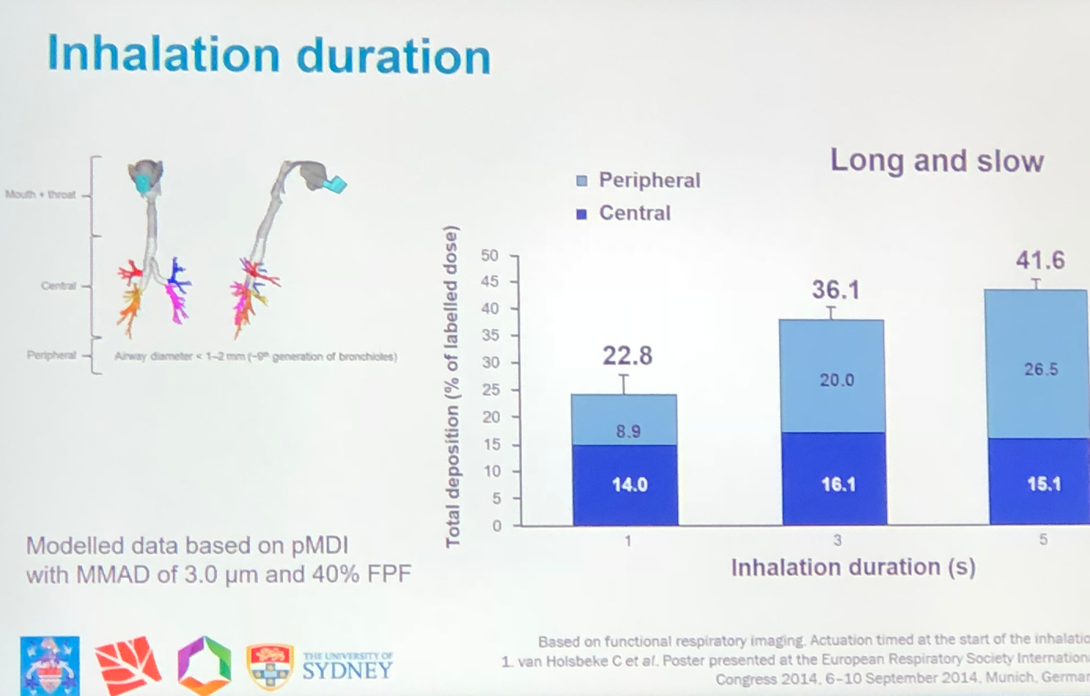
- It is important to deliver the inhaled medication to its right target. In mild to moderate asthma, ventilation is not greatly affected, however in severe asthma there are many ventilation abnormalities which seem to be fixed, perhaps as a consequence of small airways remodelling.
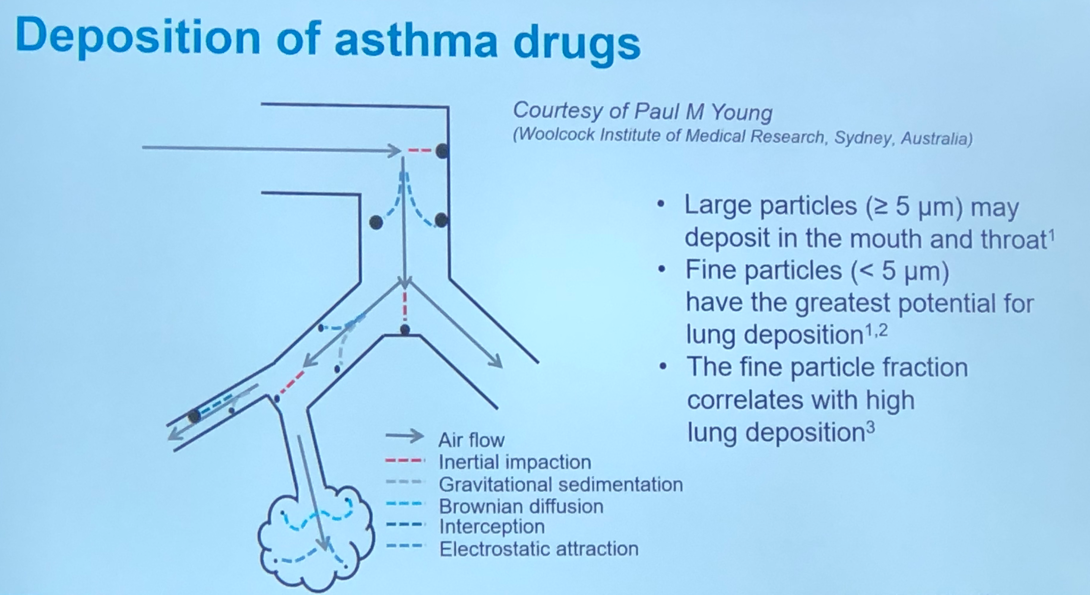
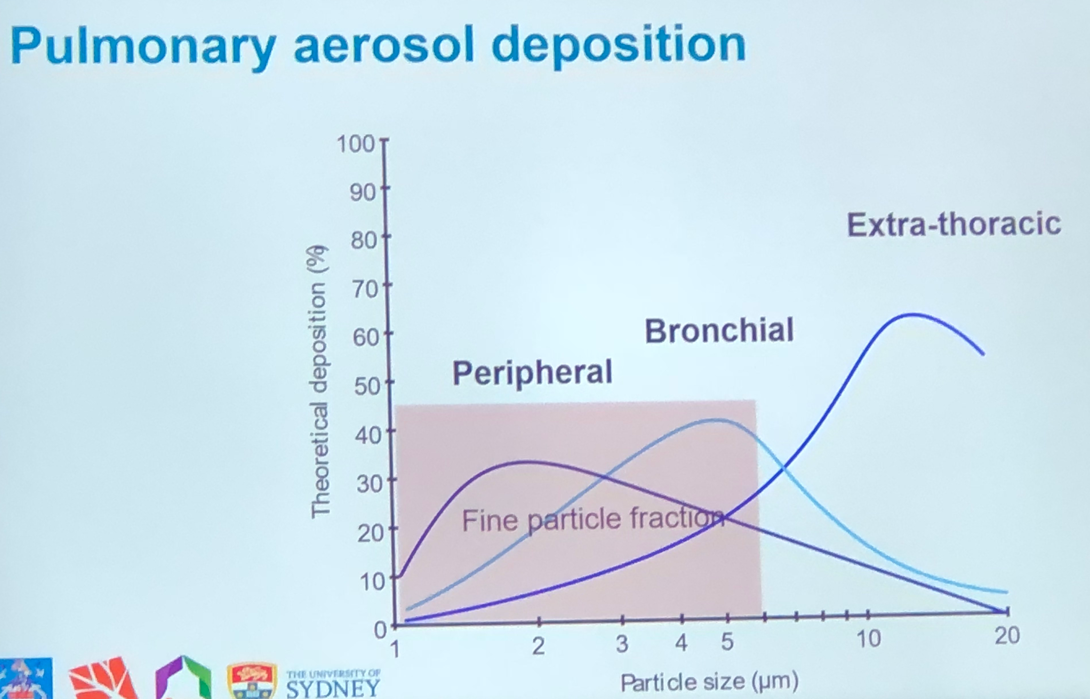
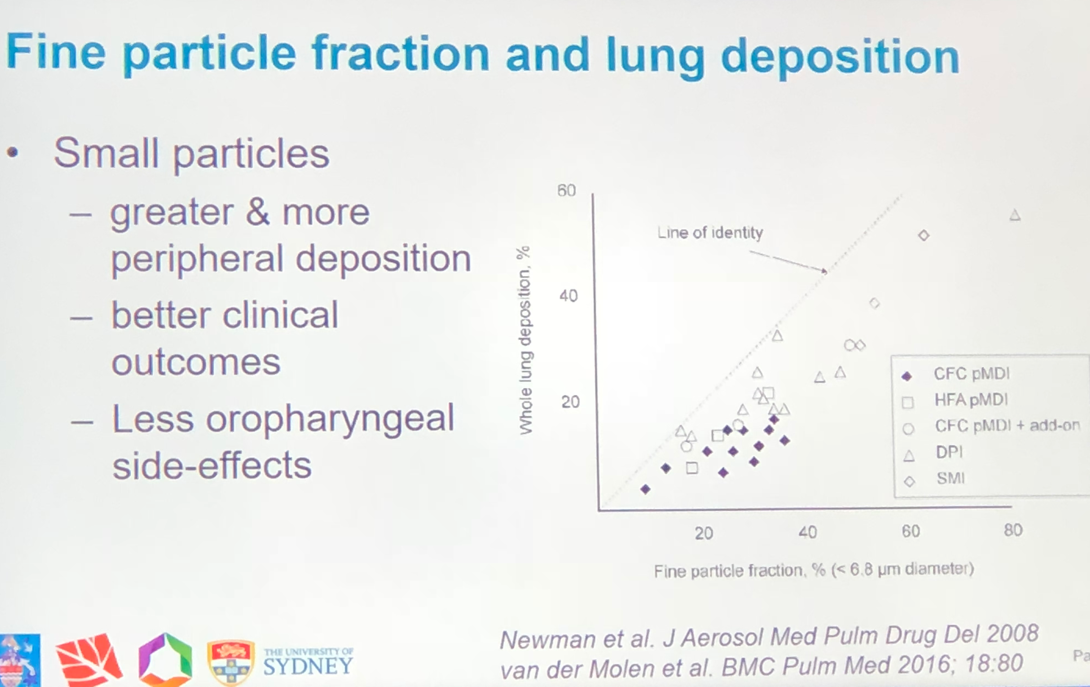
- Large particles tend to be deposited in the mouth and throat due to inertial impaction. Fine particles (<5 um) have the greatest potential for peripheral lung deposition, as can be seen below.
- Ideal inhaler therefore should be breath actuated, match flow rate, fine particles and continuous on demand flow
|
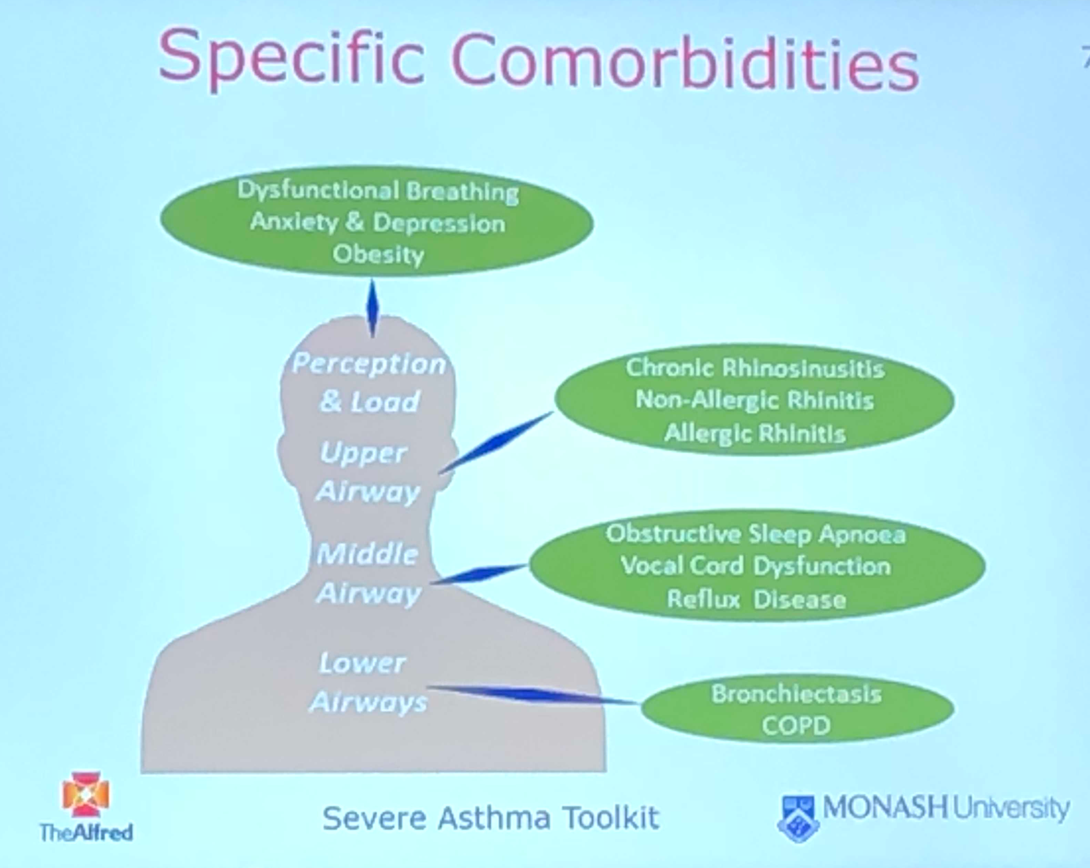
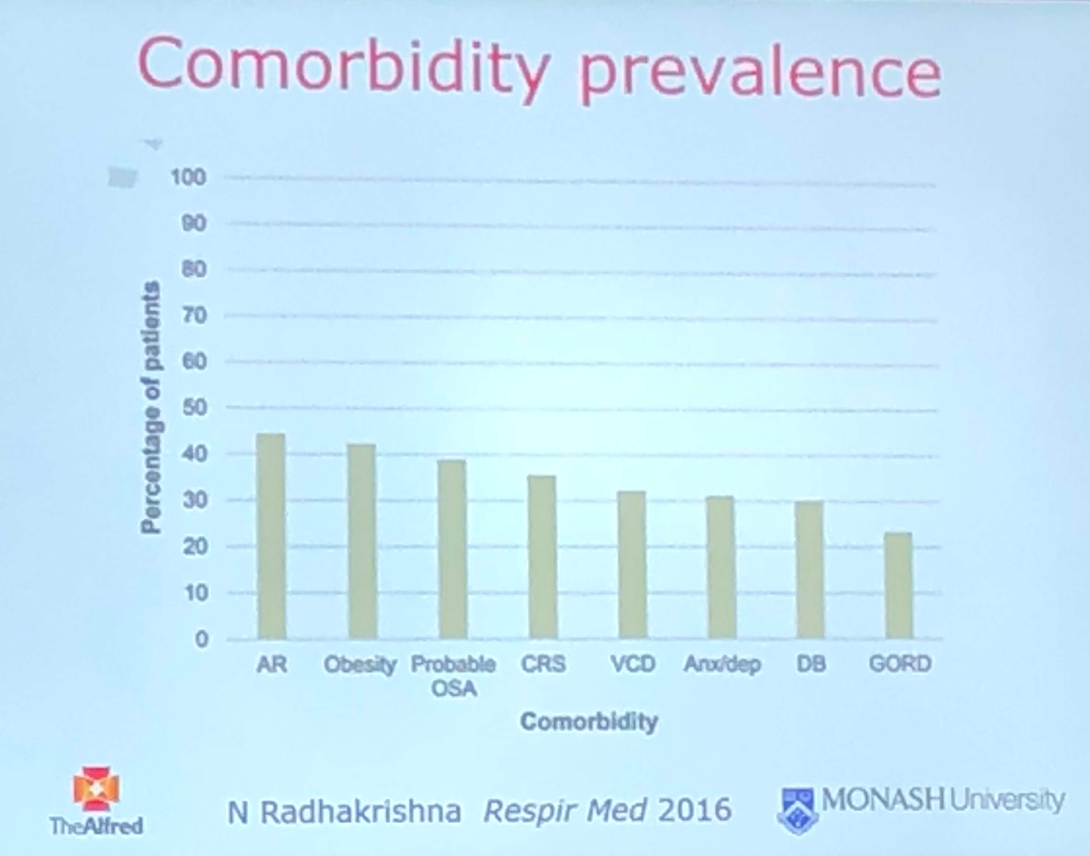
Assessment of co-morbidities
|