Question 1
With regards to peripheral vestibulopathies, what is TRUE
(A) The direction of nystagmus is away from the lesion
(B) The direction of nystagmus is towards the lesion
(C) The direction of nystagmus is orthogonal towards the lesion
(D) The direction of nystagmus is away from the lesion apart from early phase vestibular neuritis
(E) The direction of nystagmus is towards the lesion apart from early phase vestibular neuritis
D: According to RPA lecture notes. If there is a vestibulopathy, then that organ cannot provide information to the brain. Hence the brain interprets the majority of information coming from the contralateral organ as signifying movement towards that organ (that is if there is a right vestibulopathy then the brain interprets the signals as more dominant from the left organ and thinks that the head is moving towards the left). The vestibular-oscular reflex then kicks in, causing fast beating nystagmus to the direction of the organ that is working, which is the opposite organ that is affected.
Question 2
What is true about the direction of nystagmus in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
(A) Posterior canal nystagmus is characterised by torsional upbeat nystagmus
(B) Anterior canal nystagmus is characterised by upbeat square wave nystagmus
(C) Horizontal canal nystagmus is characterised by non-violent horizontal plane nystagmus
(D) Vertical canal nystagmus is characterised by down beat nystagmus
(E) Tetrahedral canal nystagmus is characterised by oscillatory nystagmus
A: Anterior canal nystagmus is characterised by torsional down beat nystagmus, horizontal canal nystagmus is characterised by violent horizontal plane nystagmus, vertical and tetrahedral canal nystagmus do not exist at all. RPA lecture notes
Question 3
In what condition do you see the following image?
With regards to peripheral vestibulopathies, what is TRUE
(A) The direction of nystagmus is away from the lesion
(B) The direction of nystagmus is towards the lesion
(C) The direction of nystagmus is orthogonal towards the lesion
(D) The direction of nystagmus is away from the lesion apart from early phase vestibular neuritis
(E) The direction of nystagmus is towards the lesion apart from early phase vestibular neuritis
D: According to RPA lecture notes. If there is a vestibulopathy, then that organ cannot provide information to the brain. Hence the brain interprets the majority of information coming from the contralateral organ as signifying movement towards that organ (that is if there is a right vestibulopathy then the brain interprets the signals as more dominant from the left organ and thinks that the head is moving towards the left). The vestibular-oscular reflex then kicks in, causing fast beating nystagmus to the direction of the organ that is working, which is the opposite organ that is affected.
Question 2
What is true about the direction of nystagmus in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
(A) Posterior canal nystagmus is characterised by torsional upbeat nystagmus
(B) Anterior canal nystagmus is characterised by upbeat square wave nystagmus
(C) Horizontal canal nystagmus is characterised by non-violent horizontal plane nystagmus
(D) Vertical canal nystagmus is characterised by down beat nystagmus
(E) Tetrahedral canal nystagmus is characterised by oscillatory nystagmus
A: Anterior canal nystagmus is characterised by torsional down beat nystagmus, horizontal canal nystagmus is characterised by violent horizontal plane nystagmus, vertical and tetrahedral canal nystagmus do not exist at all. RPA lecture notes
Question 3
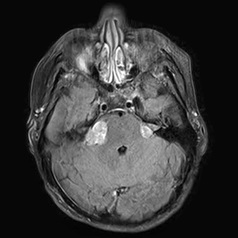
In what condition do you see the following image?
Bilateral acoustic neuromas are characteristic of which condition?
(A) NF1
(B) NF2
(C) VHL
(D) Tuberosclerosis
(E) Serpinginous carcinomatosis
B: RPA 2015
Question 4
Vertical nystagmus is characteristic of which brainstem lesion
(A) medulla
(B) cerebral aqueduct
(C) mid brain
(D) pons
(E) cerebellum
C: Vertical nystagmus is localised to the midbrain. Horizontal nystagmus localises to the pons. Cerebellar nystagmus is downbeating
(A) NF1
(B) NF2
(C) VHL
(D) Tuberosclerosis
(E) Serpinginous carcinomatosis
B: RPA 2015
Question 4
Vertical nystagmus is characteristic of which brainstem lesion
(A) medulla
(B) cerebral aqueduct
(C) mid brain
(D) pons
(E) cerebellum
C: Vertical nystagmus is localised to the midbrain. Horizontal nystagmus localises to the pons. Cerebellar nystagmus is downbeating