Question 1
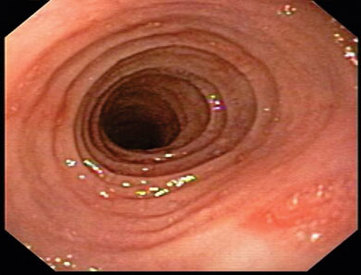
A 34 year old male has had repeated bouts of food impaction, and today he presents with the same. He has a past medical history of atopic illnesses. He undergoes an endoscopy with the results shown below:
A 34 year old male has had repeated bouts of food impaction, and today he presents with the same. He has a past medical history of atopic illnesses. He undergoes an endoscopy with the results shown below:
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment strategy?
(A) Omalizumab
(B) Antigen de-sensitisation
(C) Gluten free diet
(D) Esophageal dilatation
(E) Topical steroids such as fluticasone with concomitant 6 food elimination diet
E: Topical steroids with 6 food elimination diet would be the treatment of choice. This picture shows the typical macroscopic features of eosinophilic oesophagitis, which is an increasingly recognised entity. Histology would reveal the presence of eosinophils (>15 per hfu) in a mucosa otherwise devoid of this cell lineage. Omalizumab is an anti-IgE monoclonal antibody and has no effect on the disease course of eosinophilic oesophagitis. The pathogenesis relates to chronic antigen exposure, perhaps through increased leakiness of tight junctions in the squamous epithelium of the oesophagus. Eosinophils are recruited, driven largely by a Th2 response and secretion of IL-13. In addition, IL-13 has been shown to decrease the synthesis of tight junction molecules such as desmoglein. Corticosteroids decrease IL-13 secretion and hence are effective in this condition. Treatment is long term as the pathogenesis is chronic. N Engl J Med 2015; 373:1640-1648
(A) Omalizumab
(B) Antigen de-sensitisation
(C) Gluten free diet
(D) Esophageal dilatation
(E) Topical steroids such as fluticasone with concomitant 6 food elimination diet
E: Topical steroids with 6 food elimination diet would be the treatment of choice. This picture shows the typical macroscopic features of eosinophilic oesophagitis, which is an increasingly recognised entity. Histology would reveal the presence of eosinophils (>15 per hfu) in a mucosa otherwise devoid of this cell lineage. Omalizumab is an anti-IgE monoclonal antibody and has no effect on the disease course of eosinophilic oesophagitis. The pathogenesis relates to chronic antigen exposure, perhaps through increased leakiness of tight junctions in the squamous epithelium of the oesophagus. Eosinophils are recruited, driven largely by a Th2 response and secretion of IL-13. In addition, IL-13 has been shown to decrease the synthesis of tight junction molecules such as desmoglein. Corticosteroids decrease IL-13 secretion and hence are effective in this condition. Treatment is long term as the pathogenesis is chronic. N Engl J Med 2015; 373:1640-1648