Question 1
What is true about the epidemiology of lung cancer in Australia
(A) The incidence in males is rising whilst the incidence in females has stabilised
(B) It is the fourth most common cause of cancer but the leading cause of cancer related death
(C) It accounts for the highest health expenditure in non-caucasian Australians
(D) Large cell cancer is more common than small cell cancer
(E) Squamous cancer is the commonest histopathological subtype of lung cancer
B: RPA lecture notes: The incidence is rising in females as this follows the trends of smoking. Adenocarcinoma is the commonest cause of lung cancer in Australia now. It is a sub-type of non-small cell lung cancer.
Question 2
What biomarkers are NOT important in non-small cell lung cancer
(A) EML-ALK re-arrangement
(B) EGFR1 mutations
(C) PD1 ligand expression
(D) KRAS mutations
(E) ROS1 gene rearrangements
C: Regardless of PD1 ligand expression, nivolumab appears to have efficacy in squamous and non-squamous NSCLC. ROS1 gene re-arrangements have been found to be predictive of response to crizotinib. N Engl J Med 2015; 373:123-135, N Engl J Med 2015; 373:1627-1632, N Engl J Med 2014; 371:1963-1971
Question 3
A 51 year old female from Dubbo is electively admitted for investigation of a lung lesion. She has a CT scan that shows a large right sided lung lesion with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. What is the reason for organising a PET CT?
(A) PET-scan helps to rule out stage 4 disease
(B) PET scan will best elucidate fatal cranial disease
(C) PET scan will highlight bone disease far better
(D) PET scan result will help determine response to erlotinib
(E) PET scan is predictive of the T790M gatekeeper mutation
A: RPA course, helps to rule out metastatic disease.
Question 4
What epidemiological feature is most in keeping with a patient with EGFR activating mutations?
(A) Asian, smoker, female
(B) Non-asian, smoker, female
(C) non-asian, non-smoker, male
(D) Asian, non-smoker, male
(E) Asian, non-smoker, female
E: RPA course 2015
Question 5
What epidemiological feature is most in keeping with a patient with EML-ALK gene re-arrangement?
(A) Asian, male, non-smoker
(B) Asian, female, non-smoker
(C) Non-asian, male, non-smoker
(D) Non-asian, female, smoker
(E) Asian, female, smoker
A: RPA course 2015
Question 6
What is the most common side-effect of erlotinib?
(A) Fatigue
(B) Rash
(C) Anorexia
(D) Nausea
(E) Stomatitis
A: All the above are side effects that occurred more commonly in patients treated with erlotinib however fatigue (at 79%) was more common than rash (76%). N Engl J Med 2005; 353:123-132
Question 7
According to the PBS, what group of patients are ineligible to receive erlotinib?
(A) EGFR activating mutations
(B) EML-4 ALK rearrangement mutations
(C) Patients whose WHO functional class is > 2
(D) Patients who have had previous exposure to chemotherapy
(E) Patients who are found to be stage 3B
C: The current PBS guidelines exclude WHO class > 2
Question 8
What is the level of positive cells, as determined by fluorescence in-situ hybridisation, that are required in order to qualify for crizotinib treatment?
(A) 10%
(B) 15%
(C) 20%
(D) 25%
(E) 30%
B: A FISH + for EML4-ALK break apart gene re-arrangement is required for PBS funding of crizotinib. The number of cells required are > 15% (pbs.gov.au)
Question 9
What is NOT a common side-effect of crizotinib
(A) Vision disturbance
(B) Diarrhoea
(C) Oedema
(D) Thrombocytopenia
(E) Vomiting
D: All the above are common apart from thrombocytopenia (only 1%). Visual disturbance was the most common side effect. N Engl J Med 2014; 371:2167-2177.
Question 10
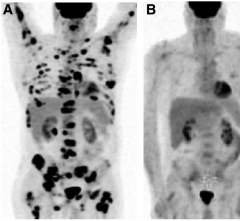
A 62 year old man from Lismore presents with weight loss, night sweats and chest pain. A chest x-ray initially reveals a large spiculated lesion in the chest. He underwent a PET scan (left image) which is shown below. Biopsy revealed adenocarcinoma of the lung with EGFR mutation, negative EML4-ALK FISH study.
What is true about the epidemiology of lung cancer in Australia
(A) The incidence in males is rising whilst the incidence in females has stabilised
(B) It is the fourth most common cause of cancer but the leading cause of cancer related death
(C) It accounts for the highest health expenditure in non-caucasian Australians
(D) Large cell cancer is more common than small cell cancer
(E) Squamous cancer is the commonest histopathological subtype of lung cancer
B: RPA lecture notes: The incidence is rising in females as this follows the trends of smoking. Adenocarcinoma is the commonest cause of lung cancer in Australia now. It is a sub-type of non-small cell lung cancer.
Question 2
What biomarkers are NOT important in non-small cell lung cancer
(A) EML-ALK re-arrangement
(B) EGFR1 mutations
(C) PD1 ligand expression
(D) KRAS mutations
(E) ROS1 gene rearrangements
C: Regardless of PD1 ligand expression, nivolumab appears to have efficacy in squamous and non-squamous NSCLC. ROS1 gene re-arrangements have been found to be predictive of response to crizotinib. N Engl J Med 2015; 373:123-135, N Engl J Med 2015; 373:1627-1632, N Engl J Med 2014; 371:1963-1971
Question 3
A 51 year old female from Dubbo is electively admitted for investigation of a lung lesion. She has a CT scan that shows a large right sided lung lesion with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. What is the reason for organising a PET CT?
(A) PET-scan helps to rule out stage 4 disease
(B) PET scan will best elucidate fatal cranial disease
(C) PET scan will highlight bone disease far better
(D) PET scan result will help determine response to erlotinib
(E) PET scan is predictive of the T790M gatekeeper mutation
A: RPA course, helps to rule out metastatic disease.
Question 4
What epidemiological feature is most in keeping with a patient with EGFR activating mutations?
(A) Asian, smoker, female
(B) Non-asian, smoker, female
(C) non-asian, non-smoker, male
(D) Asian, non-smoker, male
(E) Asian, non-smoker, female
E: RPA course 2015
Question 5
What epidemiological feature is most in keeping with a patient with EML-ALK gene re-arrangement?
(A) Asian, male, non-smoker
(B) Asian, female, non-smoker
(C) Non-asian, male, non-smoker
(D) Non-asian, female, smoker
(E) Asian, female, smoker
A: RPA course 2015
Question 6
What is the most common side-effect of erlotinib?
(A) Fatigue
(B) Rash
(C) Anorexia
(D) Nausea
(E) Stomatitis
A: All the above are side effects that occurred more commonly in patients treated with erlotinib however fatigue (at 79%) was more common than rash (76%). N Engl J Med 2005; 353:123-132
Question 7
According to the PBS, what group of patients are ineligible to receive erlotinib?
(A) EGFR activating mutations
(B) EML-4 ALK rearrangement mutations
(C) Patients whose WHO functional class is > 2
(D) Patients who have had previous exposure to chemotherapy
(E) Patients who are found to be stage 3B
C: The current PBS guidelines exclude WHO class > 2
Question 8
What is the level of positive cells, as determined by fluorescence in-situ hybridisation, that are required in order to qualify for crizotinib treatment?
(A) 10%
(B) 15%
(C) 20%
(D) 25%
(E) 30%
B: A FISH + for EML4-ALK break apart gene re-arrangement is required for PBS funding of crizotinib. The number of cells required are > 15% (pbs.gov.au)
Question 9
What is NOT a common side-effect of crizotinib
(A) Vision disturbance
(B) Diarrhoea
(C) Oedema
(D) Thrombocytopenia
(E) Vomiting
D: All the above are common apart from thrombocytopenia (only 1%). Visual disturbance was the most common side effect. N Engl J Med 2014; 371:2167-2177.
Question 10
A 62 year old man from Lismore presents with weight loss, night sweats and chest pain. A chest x-ray initially reveals a large spiculated lesion in the chest. He underwent a PET scan (left image) which is shown below. Biopsy revealed adenocarcinoma of the lung with EGFR mutation, negative EML4-ALK FISH study.
What is the correct treatment option?
(A) erlotinib
(B) imatinib
(C) nivolumab
(D) crizotinib
(E) lung resection
A: stage 4 adenocarcinoma with EGFR +, ALK gene re-arrangement -. Nivolumab is also an option but not licensed in Australia
Question 11
What is the most common type of mutation in non small cell lung cancer?
(A) EGFR
(B) KRAS
(C) ROS1
(D) p53
(E) EML4-ALK rearrangement
B: Predicts resistance to targeted therapies (RPA lecture series)
Question 12
A 67 year old Asian female is diagnosed with stage 4 adenocarcinoma of the lung. Driver mutation testing identifies an EGFR mutation. She is subsequently started on erlotinib. 3 weeks after she describes an acneform rash on her face and torso, which is pruritic and tender. It has severely impacted on her self esteem and she does not want to go outside for fear of embarrassment. What is the most appropriate treatment initially for this patient?
(A) Cease TKI
(B) Emollients and topical steroids
(C) doxycycline, topical steroids and emollients
(D) transretinoin
(E) topical erythromycin
C: This is a grade 3 TKI rash. If rash does not improve with these measures then the TKI should be stopped until the rash improves to grade 1 and consideration of dose reduction made. RPA Course 2015
Question 13
Which of the following is NOT a well known side effect of Crizotinib?
(A) Light/ dark adjustment
(B) QT prolongation
(C) Hepatic enzyme elevation
(D) Pneumonitis
(E) Colitis
E: Visual disturbances are a common side effect of Crizotinib, which inhibits the action of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase. It is hypothesised that this molecule binds to rods and cones. The effect is short lived. Pneumonitis occurs in less than 2% of patients. Colitis is not a well known side-effect. RPA course 2015
(A) erlotinib
(B) imatinib
(C) nivolumab
(D) crizotinib
(E) lung resection
A: stage 4 adenocarcinoma with EGFR +, ALK gene re-arrangement -. Nivolumab is also an option but not licensed in Australia
Question 11
What is the most common type of mutation in non small cell lung cancer?
(A) EGFR
(B) KRAS
(C) ROS1
(D) p53
(E) EML4-ALK rearrangement
B: Predicts resistance to targeted therapies (RPA lecture series)
Question 12
A 67 year old Asian female is diagnosed with stage 4 adenocarcinoma of the lung. Driver mutation testing identifies an EGFR mutation. She is subsequently started on erlotinib. 3 weeks after she describes an acneform rash on her face and torso, which is pruritic and tender. It has severely impacted on her self esteem and she does not want to go outside for fear of embarrassment. What is the most appropriate treatment initially for this patient?
(A) Cease TKI
(B) Emollients and topical steroids
(C) doxycycline, topical steroids and emollients
(D) transretinoin
(E) topical erythromycin
C: This is a grade 3 TKI rash. If rash does not improve with these measures then the TKI should be stopped until the rash improves to grade 1 and consideration of dose reduction made. RPA Course 2015
Question 13
Which of the following is NOT a well known side effect of Crizotinib?
(A) Light/ dark adjustment
(B) QT prolongation
(C) Hepatic enzyme elevation
(D) Pneumonitis
(E) Colitis
E: Visual disturbances are a common side effect of Crizotinib, which inhibits the action of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase. It is hypothesised that this molecule binds to rods and cones. The effect is short lived. Pneumonitis occurs in less than 2% of patients. Colitis is not a well known side-effect. RPA course 2015